Peptides stand today as the most-talked-about frontier in longevity science. The category now spans legitimate medicine and early-stage research. It ranges from blockbuster pharmaceutical drugs to experimental compounds sold online as “research use only” in loosely regulated gray markets.
Among the most discussed peptides in 2026 are MOTS-c and BPC-157. Both are described in online forums as powerful tools for metabolic health, tissue repair, and even lifespan extension. They sit within a broader wave of emerging peptide trends that researchers and clinicians are still trying to place on the spectrum between experimental biology and mainstream medicine. Yet, when you look closely at the human data, the story becomes far more nuanced.
MOTS-c is a mitochondrial-derived peptide, meaning it originates from the energy-producing structures inside our cells. Early research suggests it plays a role in metabolic regulation. BPC-157, often nicknamed the “Wolverine peptide” in fitness circles, is promoted for rapid healing and recovery. But neither is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for general medical use, and both appear on the FDA’s list of bulk drug substances that may present significant safety risks when used in compounding, citing concerns such as immunogenicity, impurities, and limited human exposure data.
That tension between promising biology and limited clinical evidence is what makes these peptides so compelling and so controversial. To understand where MOTS-c and BPC-157 truly stand, the implications can seem abstract. It helps to step back and apply a structured way of evaluating scientific claims.

Longevity Peptides Defined: Core Facts About MOTS-c and BPC-157
These core, data-grounded facts provide the essential baseline for evaluating longevity peptide safety and performance regarding peptide science health applications and safety.
- MOTS-c is real biology: It is encoded within mitochondrial DNA and has been shown in laboratory studies to influence metabolic pathways such as AMPK signaling, which is involved in energy balance and insulin sensitivity.
- The original discovery work is documented in a foundational 2015 study. This research described MOTS-c as a mitochondrial-derived peptide that regulates insulin sensitivity and metabolic homeostasis. This pattern mirrors how regulators like NAD⁺ are tracked across aging, mapping core metabolic players in detail long before they become medicines.
- Human studies primarily track endogenous MOTS-c levels: These researchers observe naturally produced MOTS-c during exercise or metabolic stress. They rarely test MOTS-c as a direct medical treatment.
- One human study found that exercise can raise circulating levels, which supports its biological relevance but doesn’t show that injections make health outcomes better.
- BPC-157 has extensive preclinical literature: Animal and cell studies suggest potential roles in tissue repair and inflammation modulation.
- However, a comprehensive review published in 2025 emphasized that the majority of this evidence remains preclinical, meaning it was not conducted in large, well-controlled human trials.
- Human data for BPC-157 is limited and low-certainty: Small case reports and pilot studies exist, including investigations into knee pain, but these do not rise to the level of large randomized controlled trials.
- Neither peptide is FDA-approved: According to the U.S. Department of Defense’s Operation Supplement Safety program, BPC-157 is classified as an unapproved drug and is not recognized as a lawful dietary supplement ingredient.
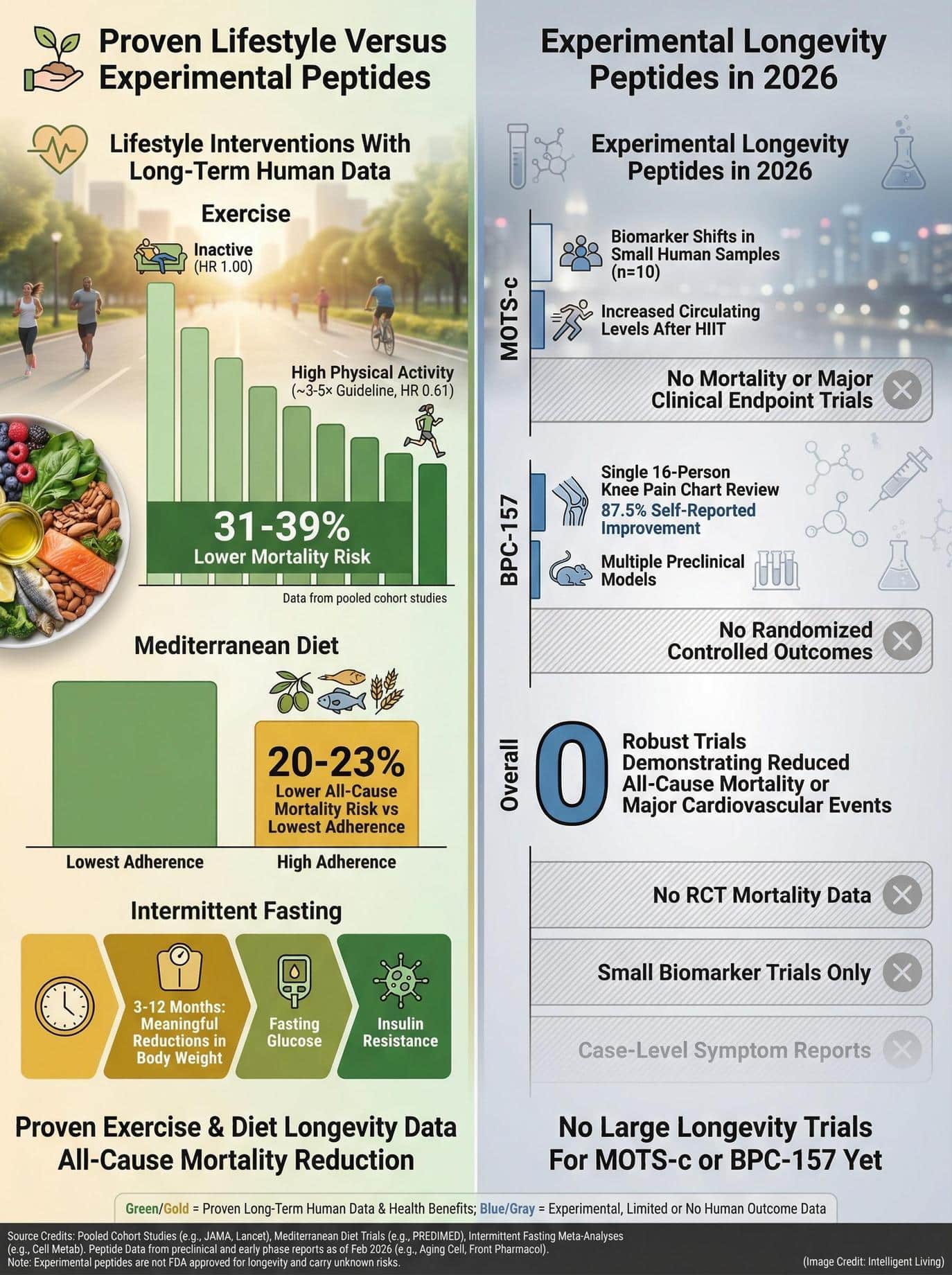
- Other longevity strategies possess more robust human data: Proven methods, including NMN and resveratrol strategies or Mediterranean Diet 3.0 protocols, rely on multiple human trials and biomarker analyses.
- However, they still fall short of being guaranteed longevity solutions.
These facts form the baseline. Everything else in the conversation about peptide biohacking needs to be evaluated in light of them.

The Clinical Evidence Ladder: Evaluating Longevity Peptide Scientific Claims
Scientific excitement often moves faster than clinical proof. Separating compelling laboratory findings from medically actionable evidence requires an evidence ladder. This structure mirrors how nutrition research reshapes dietary guidelines to provide data-driven recommendations.
Understanding The Rungs of Scientific Proof
At the ladder’s base, you find basic biology. Here, researchers identify a molecule and map its structure, exploring exactly how it interacts with living cells. MOTS-c sits comfortably on this rung. Its mitochondrial origin and metabolic signaling role are well-documented in peer-reviewed literature.
The next rung involves animal studies. Many peptides, including BPC-157, have extensive animal data suggesting effects on wound healing, inflammation, and tissue regeneration. These results can be promising, but animal physiology is not identical to human physiology. Positive outcomes in rodents do not automatically translate into safe and effective therapies for people.
From Early Observations to Clinical Standards
Above that are early human studies. These may include small pilot trials, case series, or biomarker observations. For MOTS-c, this largely involves studies of naturally occurring levels in response to exercise. For BPC-157, it includes limited human reports with small sample sizes.
Near the top are large randomized controlled trials, the gold standard for determining whether a therapy truly works and is safe across diverse populations. For both MOTS-c and BPC-157, this rung remains largely unoccupied. Current senomorphic strategies for age-related muscle loss illustrate how therapies move through this ladder into carefully staged safety trials.
Finally, at the top is regulatory approval and post-market surveillance, where a therapy has demonstrated sufficient safety and effectiveness to be formally approved, and its long-term risks are continuously monitored. Neither MOTS-c nor BPC-157 has reached this stage.
When readers encounter bold claims about longevity peptides, asking “Which rung of the ladder does this sit on?” is often more useful than asking whether the molecule sounds impressive.
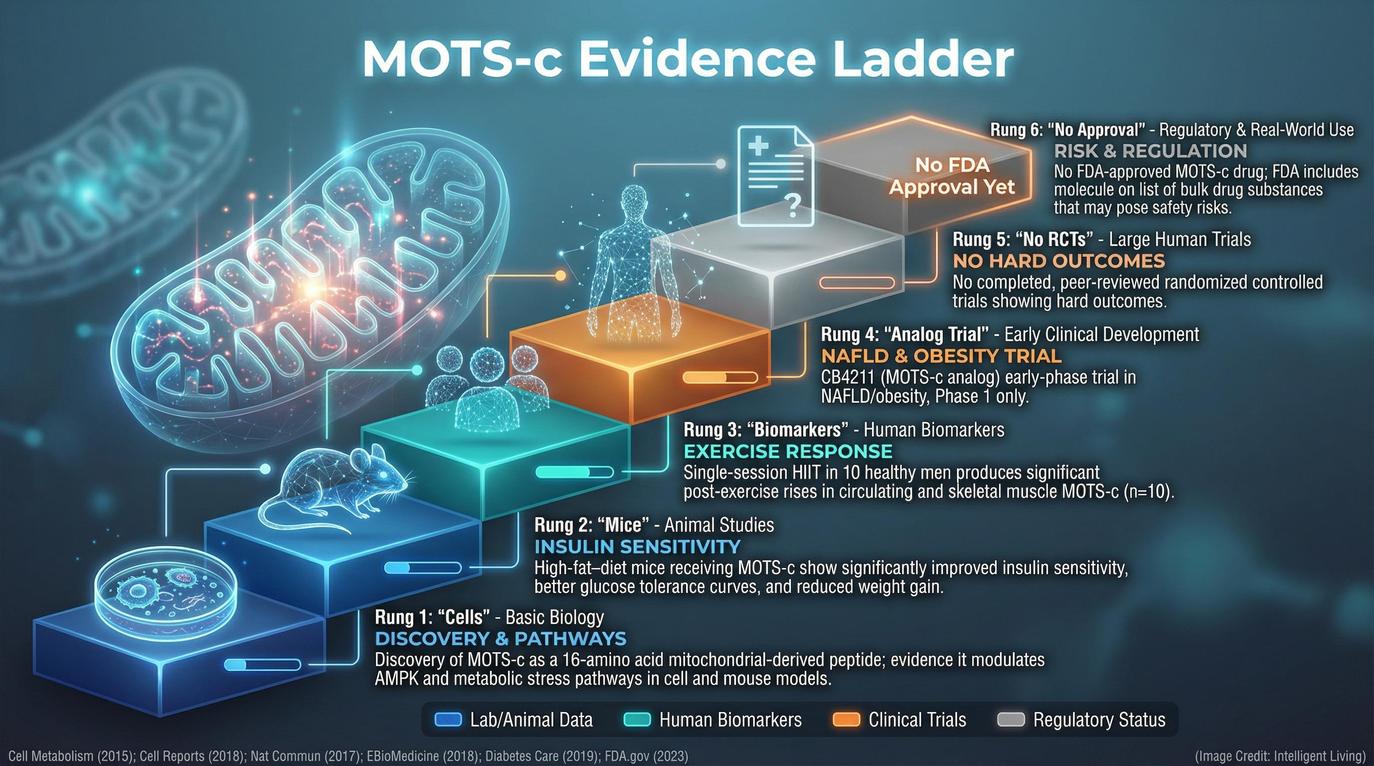
MOTS-c Mitochondrial Biology: Assessing Metabolic Health and Human Clinical Data
While we often call mitochondria cellular power plants, they function more like critical signaling hubs for the entire body. MOTS-c is a short peptide encoded within mitochondrial DNA. This surprising discovery revealed a new pathway for mitochondrial signaling and systemic cellular communication.
Mitochondrial Signaling and Metabolic Homeostasis
Early research demonstrated that MOTS-c activates pathways like AMPK. This process helps regulate glucose metabolism and energy use, promoting metabolic homeostasis and potentially reducing diet-induced insulin resistance.
Evidence from Human Exercise and Biomarker Trials
Human studies have added another layer. In one clinical exercise trial, researchers observed that endurance training increased circulating levels in blood. This suggests that MOTS-c may be part of the body’s adaptive response to physical stress. A recent review of MOTS-c biology summarizes how this 16-amino-acid peptide influences stress responses and aging. However, this type of study measures correlation; it does not demonstrate that injecting synthetic MOTS-c into humans produces equivalent or superior metabolic benefits.
There has also been clinical development of an analog known as CB4211, which appears in federal clinical trial records. Early-stage trial disclosures referenced tolerability issues like persistent injection-site reactions. Because an analog is not identical to the naturally occurring peptide, early-phase trials primarily assess safety rather than proving long-term effectiveness.
Taken together, MOTS-c represents compelling cellular biology with intriguing human biomarker data. What it does not yet represent is a proven, approved therapy for longevity or metabolic disease.
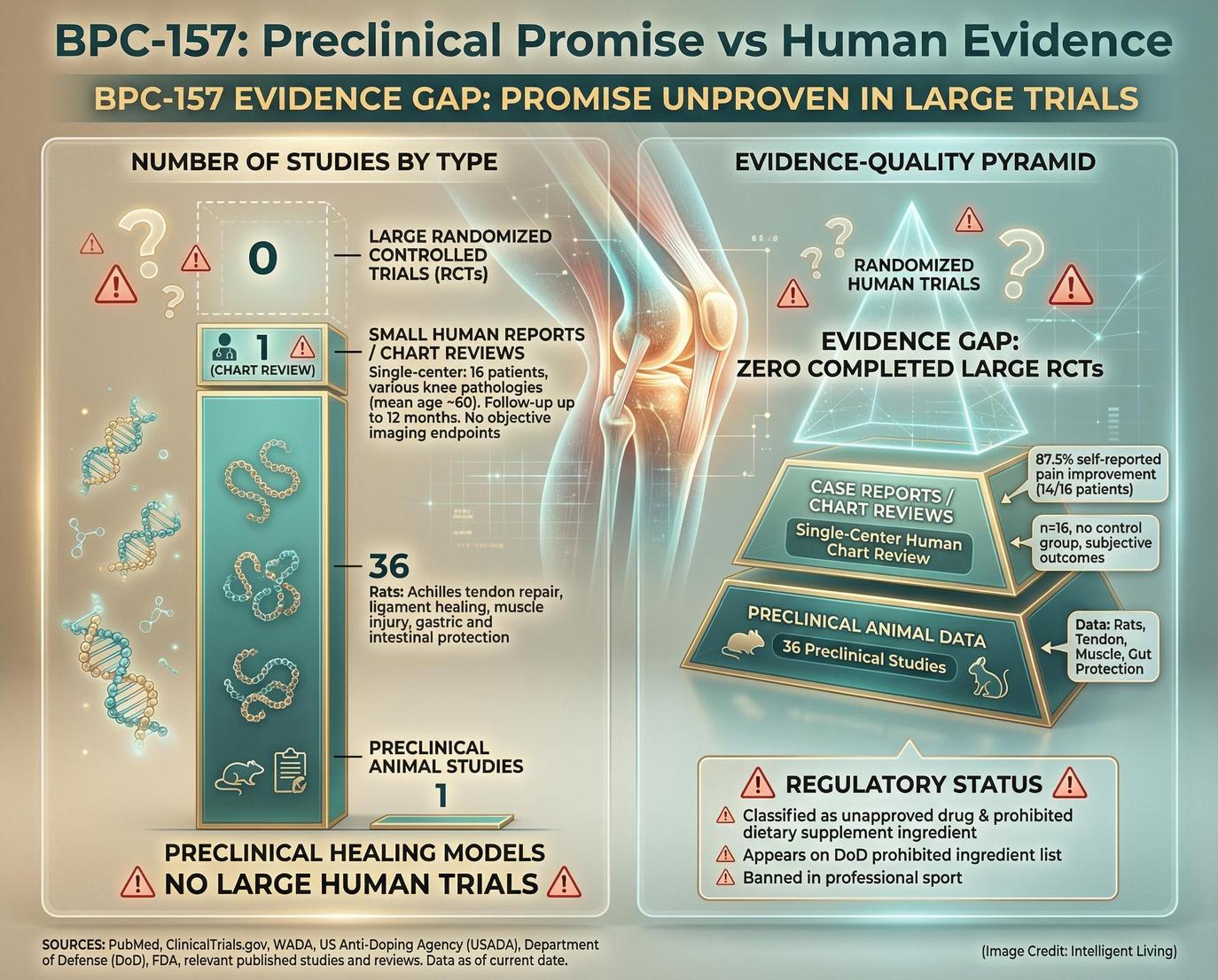
BPC-157 Regenerative Repair: Preclinical Healing Lore Versus Human Evidence
Online communities often hail BPC-157 as a regenerative breakthrough. Much of this reputation stems from animal research showing accelerated healing in tendons, ligaments, and other vital tissues.
Preclinical Research in Musculoskeletal Models
A 2024 musculoskeletal healing narrative review summarized decades of preclinical work and acknowledged the breadth of laboratory findings. However, the authors also emphasized the limited scope of controlled human trials.
Analyzing The Gaps in Clinical Trial Data
Some human evidence does exist. A knee-pain intra-articular study examined specific usage in small patient groups. While the results were described as promising, the study size and design limit how confidently those findings can be generalized.
More striking is the gap in publicly available trial-grade data. A Phase 1 study record notes that results were recalled before quality control review. That detail alone highlights how incomplete the human evidence base remains.
Regulatory context adds another layer. Stringent regulatory oversight introduces critical safety considerations for those exploring BPC-157. The Department of Defense’s Operation Supplement Safety program states that BPC-157 is an unapproved drug rather than a lawful dietary ingredient.
In the end, BPC-157 relies on a narrative built more on animal repair models and anecdotal enthusiasm than clinical proof. For readers interested in data-driven longevity, the central question is whether current evidence justifies the certainty with which these molecules are often marketed. At present, the answer requires caution, context, and a clear-eyed view of the evidence ladder.
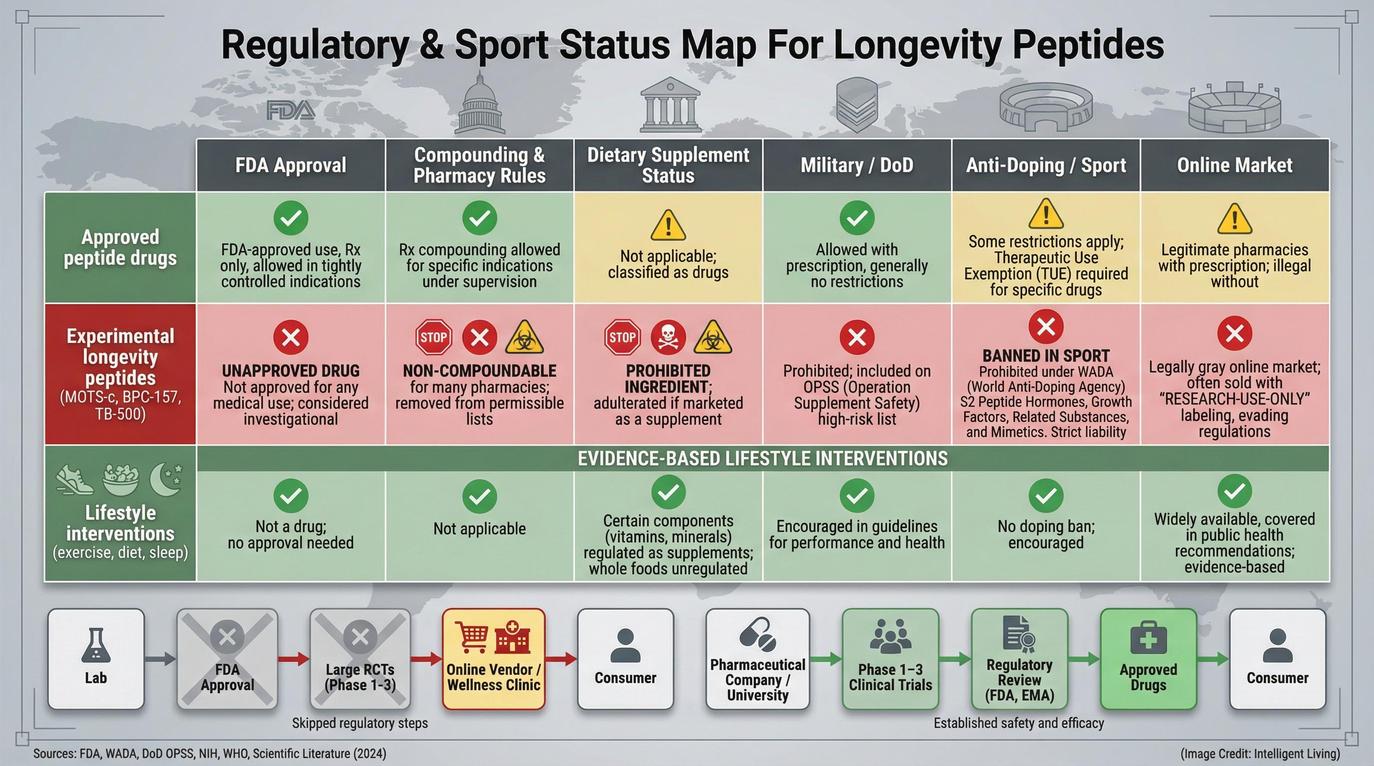
FDA Regulation and Quality Control: The Safety Risks of Compounded Peptides
When people hear that a substance appears on an FDA list, the implications can seem abstract. In practical terms, FDA scrutiny centers on safety, manufacturing standards, and whether there is enough reliable human data to justify medical use.
Compounding Risks and Regulatory Oversight Challenges
Both peptides appear on the FDA list of bulk drug substances that may present significant safety risks. The concerns listed include potential immunogenicity—the possibility that the immune system could react unpredictably—as well as challenges around purity. Because peptides are delicate chains of amino acids, even tiny manufacturing variations can disrupt their stability or biological activity.
Usually, a lack of approval signals a deeper problem: insufficient evidence, lingering safety questions, or a mix of both. This distinction is vital: clinical availability is never a substitute for formal regulatory validation. Formal FDA compounding guidance explains that compounded drugs are not evaluated for safety or effectiveness before they are marketed.
Anti-Doping Regulations: Why USADA Prohibits Longevity Peptides like MOTS-c
Groups like USADA ban these experimental peptides. They see them as pharmacologically active, unapproved, and too risky for sport.
USADA prohibits BPC-157 as an unapproved substance and explains that it lacks approval for human clinical use. Similarly, MOTS-c is banned in sport because it is not an approved therapeutic drug. These listings signal that the compounds are considered pharmacologically active enough to influence physiology without robust safety data.
The Longevity Hype Pipeline: How Research Peptides Enter the Consumer Market
Understanding why peptides like BPC-157 and MOTS-c gain traction so quickly requires examining how scientific findings move through culture.
From Preclinical Labs to Viral Social Media Trends
The cycle typically starts in preclinical labs, where researchers observe striking effects in animal models. These findings are then summarized in simplified language across blogs and podcasts. Over time, the narrative shifts. It moves from ‘this worked in rodents’ to ‘this could transform recovery’—or even, ‘this may extend lifespan.’ The story often feels settled long before products appear labeled as ‘for research use only.’
Journalistic investigations into injectable peptide trends have examined the enthusiasm around compounds like BPC-157 and TB-500 alongside their uncertain risk profiles. Experimental peptides circulate through online vendors with minimal consumer understanding of their long-term safety.
The primary bottleneck in this pipeline remains the rigorous demand for large-scale human trials. Randomized controlled studies require funding and time, while social media cycles operate on a much shorter timeline.
A Reality-Check Checklist for Evaluating Longevity Peptide Safety
Navigating the peptide market requires a disciplined approach. Before considering any experimental therapy, use this checklist to verify scientific claims:
- Verify regulatory status: Check if the substance is FDA-approved or listed as unapproved on official agency pages.
- Analyze the evidence level: Determine if claims rely on large trials or small case reports.
- Distinguish biomarkers from outcomes: Recognize that biomarker-based health monitoring can signal exploratory trends but does not always prove hard clinical outcomes.
- Evaluate manufacturing variables: Injectable substances require strict sterility and purity.
- Prioritize proven fundamentals: Factors like how the gut microbiota influences skeletal muscle underscore how lifestyle influences the same tissues many peptides aim to target.
The appeal of cutting-edge science should never obscure the value of proven health fundamentals.

Longevity Peptides in 2026: The Data-Driven Bottom Line on Human Evidence
MOTS-c and BPC-157 illustrate a broader pattern in the longevity space. Fascinating cellular biology can generate legitimate scientific curiosity, seen in epitalon lifespan narratives that weave mechanistic findings into broad promises. Yet, curiosity is not clinical confirmation.
Future Research Directions for Longevity Peptide Therapeutics
MOTS-c represents an intriguing example of mitochondrial signaling with measurable human biomarker data. It sits alongside NAD⁺ pathway support strategies as a focal point in cellular longevity. Neither peptide meets the gold standard yet. They aren’t proven, evidence-backed longevity therapies.
As we move through 2026, the divide between peptide marketing enthusiasm and clinical confirmation remains a central challenge. Today, the gap between hype and human data remains significant. The most intelligent position is disciplined curiosity guided by transparent evidence.
Longevity Peptides FAQ: MOTS-c, BPC-157, Safety, and FDA Approval
Is MOTS-c FDA-Approved?
No. MOTS-c is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a therapeutic drug. It appears on the FDA’s list of certain bulk drug substances that may present significant safety risks in compounding contexts.
Is BPC-157 FDA-Approved or a Legal Dietary Supplement?
BPC-157 is not FDA-approved, and the Department of Defense’s Operation Supplement Safety program states that it is an unapproved drug rather than a lawful dietary supplement ingredient.
Are there Human Clinical Trials for MOTS-c?
Human studies have examined endogenous MOTS-c levels, particularly in relation to exercise. There has also been development of an analog, CB4211, with a registered early-phase clinical trial. However, large-scale randomized controlled trials demonstrating benefits are not currently available.
Is BPC-157 Proven Safe in Humans?
Available human data comprises primarily small studies. While Phase 1 study records exist, peer-reviewed large-scale safety data is lacking. This means long-term safety is uncertain compared to aging implications of established drugs like metformin.
Why Do Anti-Doping Agencies Ban these Peptides?
Groups like USADA classify certain experimental peptides as prohibited because they are pharmacologically active and unapproved.
What Should Readers Focus on Instead of Experimental Peptides?
Prioritizing interventions with strong human evidence, such as metabolic fasting protocols or structured exercise, offers a more reliable foundation for health than untested injectable therapies.
